Study of dumps of liquidated mines using GPR remote scanning
March 28, 2012
Fig. 1. Pulling remotely managed GROT 12 along the profile over the combustion zone.
The works were carried out in areas of liquidated mines in Kuznetsk Coal Basin and Donbass mines.
The main objective of the project was to determine the combustion zones and their geometry in the plan and the depth. The formulation of the problem is related to the environmental security in areas with abandoned mines.
Fig. 2. View of the site of works and the corresponding GPR data.
GROT 12 and GROT 12E ground penetrating radars were used. The combustion zones determination using GPR method is based on the study of the temperature effect on the permittivity and the conductivity.
The value of the relative dielectric constant, which characterizes the degree of the substance polarization, is influenced by the mechanisms of these processes. However, the value of the dielectric constant of the substance depends on its aggregate state, as during the matter transformation from one state to another the density of the substance, its viscosity, and isotropism change significantly.
The dielectric constant characterizes the speed of the pulse in the medium. Conductivity determines the degree of electromagnetic pulse attenuation in the medium.
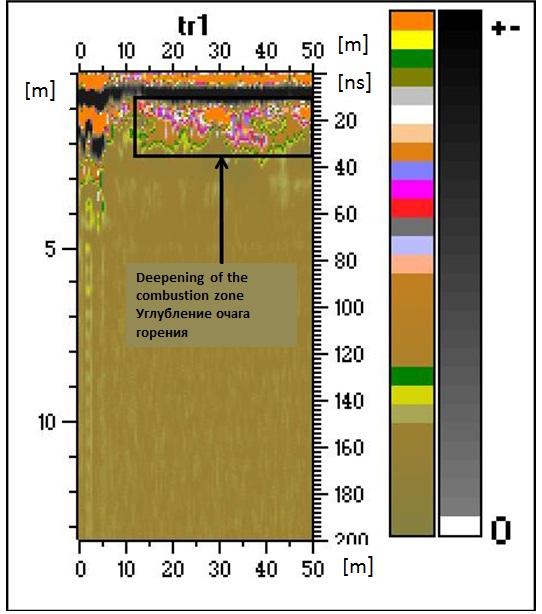
Fig. 3. Radarogram with a marked zone of deepening of the combustion.
Our objective was to compare the data of GPR measurements on the tracks on the surface of rock dumps (heaps) to the data of temperature measurements to calibrate the values of the electromagnetic parameters in accordance with the data of the temperature of rocks measurements in order to develop the algorithm to solve the inverse problem: using the GPR scanning to determine the changes of the temperature.
To study especially dangerous areas GROT 12 and GROT 12E ground penetrating radars controlled via Bluetooth were used in the mobile form.
Fig. 4. Radarogram with marked zone of maximum temperatures.